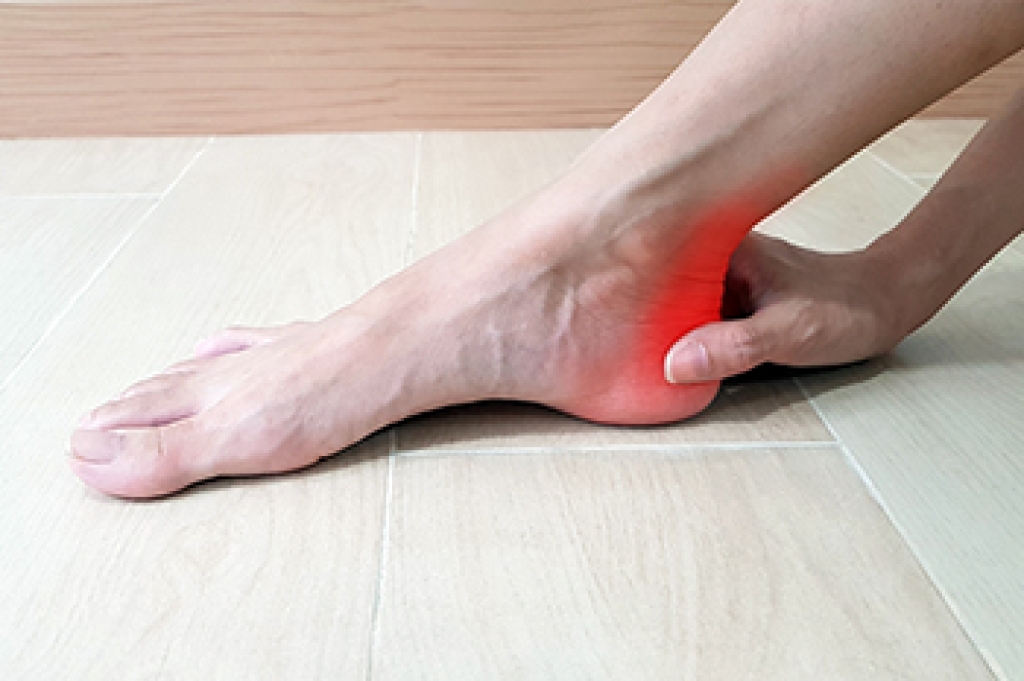
A broken toe often occurs after stubbing the foot against a hard surface, dropping a heavy object on it, or during sports activity. The toe may look swollen, bruised, or slightly crooked, and the skin can become red or tender. Many patients describe sharp pain at the time of injury, followed by throbbing discomfort that worsens while walking or wearing shoes. In some cases, movement of the toe becomes limited, and pressure along the bone increases pain. While some minor fractures can heal with protection and rest, others require more careful treatment. A podiatrist will perform a detailed examination, and may order X-rays to determine the location and severity of the break. Treatment options include protective taping, a surgical shoe, or an immobilizing cast to allow proper healing. Targeted exercises may later help restore strength and flexibility. If you have a broken toe, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for appropriate treatment.
A broken toe can be very painful and lead to complications if not properly fixed. If you have any concerns about your feet, contact one of our podiatrists from Westside Podiatry Center, LLP. Our doctors will treat your foot and ankle needs.
What to Know About a Broken Toe
Although most people try to avoid foot trauma such as banging, stubbing, or dropping heavy objects on their feet, the unfortunate fact is that it is a common occurrence. Given the fact that toes are positioned in front of the feet, they typically sustain the brunt of such trauma. When trauma occurs to a toe, the result can be a painful break (fracture).
Symptoms of a Broken Toe
- Throbbing pain
- Swelling
- Bruising on the skin and toenail
- The inability to move the toe
- Toe appears crooked or disfigured
- Tingling or numbness in the toe
Generally, it is best to stay off of the injured toe with the affected foot elevated.
Severe toe fractures may be treated with a splint, cast, and in some cases, minor surgery. Due to its position and the pressure it endures with daily activity, future complications can occur if the big toe is not properly treated.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact one of our offices located in Liverpool, Camillus, Skaneateles, Oswego, and Cicero, NY . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.